Leiden Clustering
Unsupervised Spatial Segmentation of Your Tissue
What It Does
Leiden Clustering is a sophisticated, graph-based community detection algorithm. It works by modeling your dataset as a network where each spatial spot is a node connected to its most metabolically similar neighbors. The algorithm then intelligently partitions this network to find "communities" — clusters of spots that are more similar to each other than to the rest of the tissue.
Why It's Here: Discovering Hidden Biology
This tool is designed for powerful unsupervised spatial segmentation. It can discover distinct metabolic regions within a tissue without any prior anatomical knowledge or human input. This is incredibly powerful for:
- Revealing hidden biological structures not visible by eye.
- Defining the precise boundaries of tumor microenvironments.
- Identifying zones of drug penetration and metabolic response.
What You Get: A New Metabolic Map
The primary output is a spatial map where each spot is colored by its assigned cluster ID. This effectively creates a brand new, metabolically-defined tissue map that is based purely on the molecular data.
Crucially, you also get a list of the top "marker" metabolites that have the highest average intensity within each cluster. This gives each newly discovered spatial domain a distinct molecular identity, telling you why it's different from its neighbors.
Example: Clustered Tissue
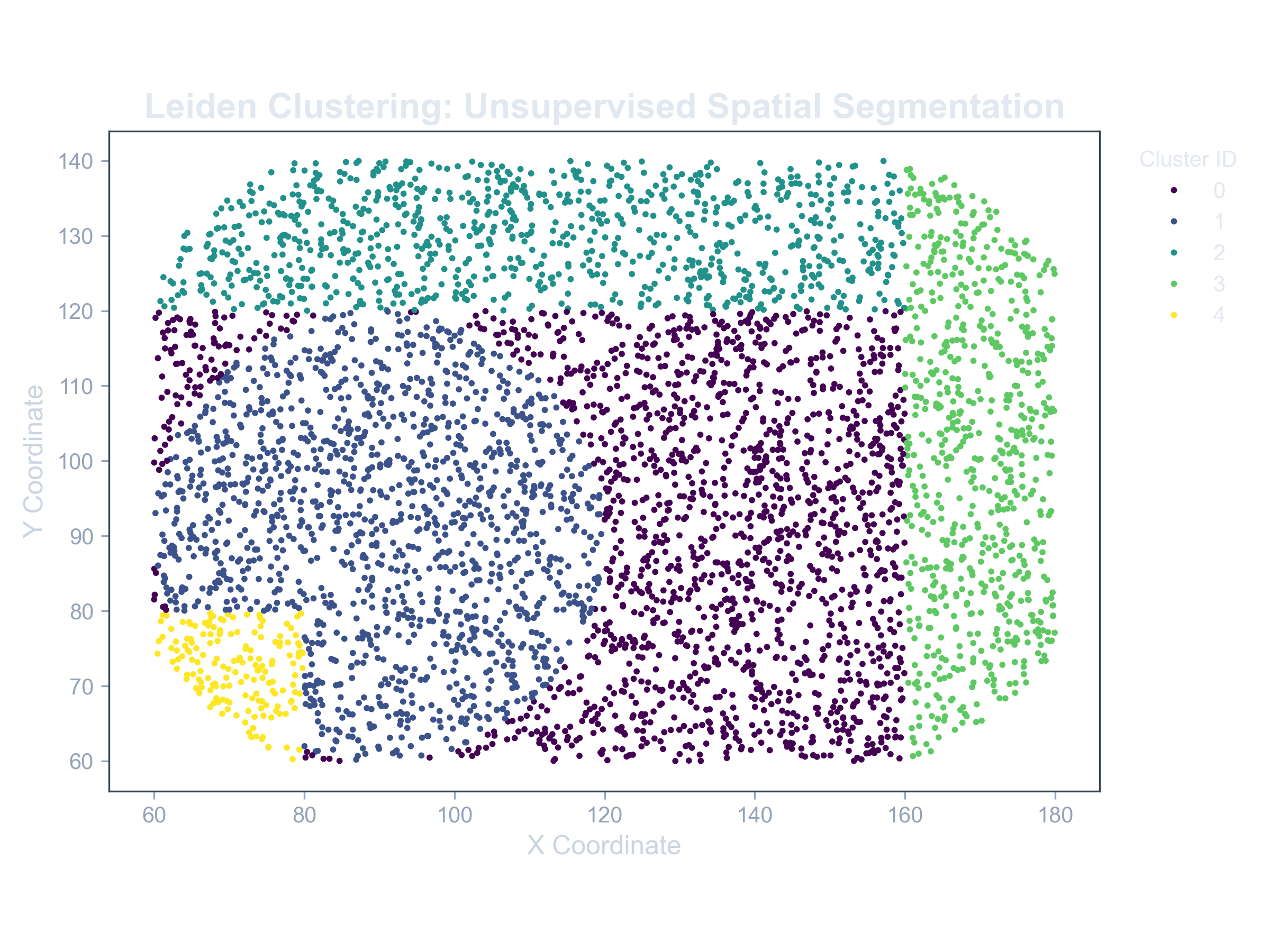
A spatial map showing distinct metabolic regions (colors) identified by the Leiden algorithm, revealing a complex microenvironment.